A blood clot or thrombus forms in one or more deep veins in the body, generally in the legs, and causes deep vein thrombosis or DVT. Leg pain or edema may be brought on by deep vein thrombosis. Since blood clots in the veins have the potential to break away, deep vein thrombosis can be serious. Once in the bloodstream, the clots have the potential to become lodged in the lungs and form clots causing an interruption in blood flow called pulmonary embolism. People can overcome PE if the clot is small and treated properly. A D-dimer test along with an MRI can help in the diagnosis of this medical condition.
Symptoms
Leg cramps, soreness or pain that frequently begins in the calf are common symptoms of DVT. According to the color of the skin, a change in the affected area’s skin tone, such as turning red or purple can also be seen as a sign of this condition. Along with this, a sense of warmth in the wounded region is often experienced by individuals with DVT.
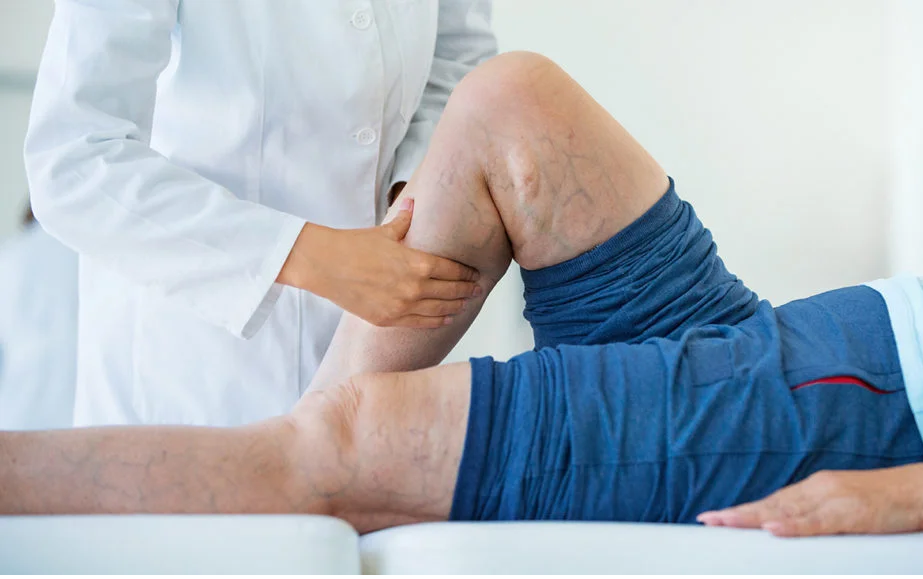
Complications
One of the most commonly observed complications of deep vein thrombosis is pulmonary embolism. Mentioned below are some of its signs:
- sudden breathlessness
- Chest discomfort or pain that gets worse when you breathe deeply or when you cough
- feeling weak or disoriented
- Fainting
- fast heartbeat
- breathing promptly
- coughing up blood
Diagnosis
A medical practitioner takes the medical history of an individual with symptoms of DVT and then prescribes a D-dimer test. If the D-Dimer test is negative, DVT can be ruled out. People who have DVT symptoms should get a well-priced D-Dimer test at a reputed pathology lab. Besides this, the following diagnostic tests can help in the diagnosis of this condition:
- Duplex Ultrasonography: Duplex ultrasonography is an imaging procedure that makes use of sound waves to examine the veins’ blood flow.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): A procedure that produces images of the body using radio waves and a magnetic field.
In some cases, there are no obvious signs of deep vein thrombosis. But if a person is experiencing some symptoms, they should make sure that they visit a medical practitioner for immediate medical attention.

Leave a comment